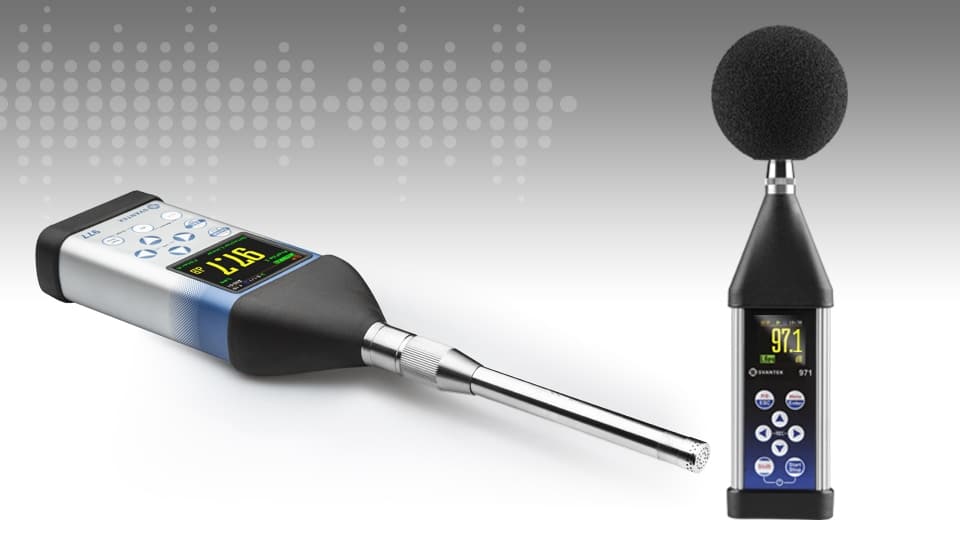
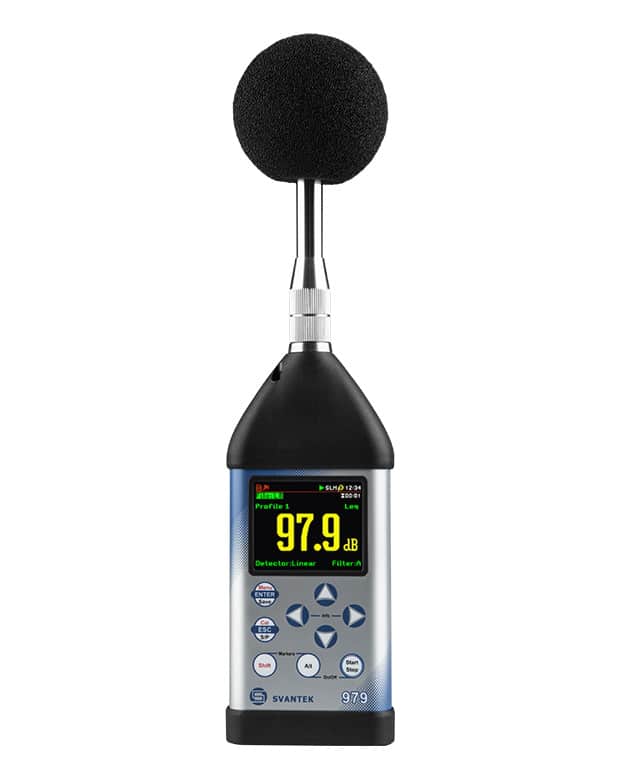
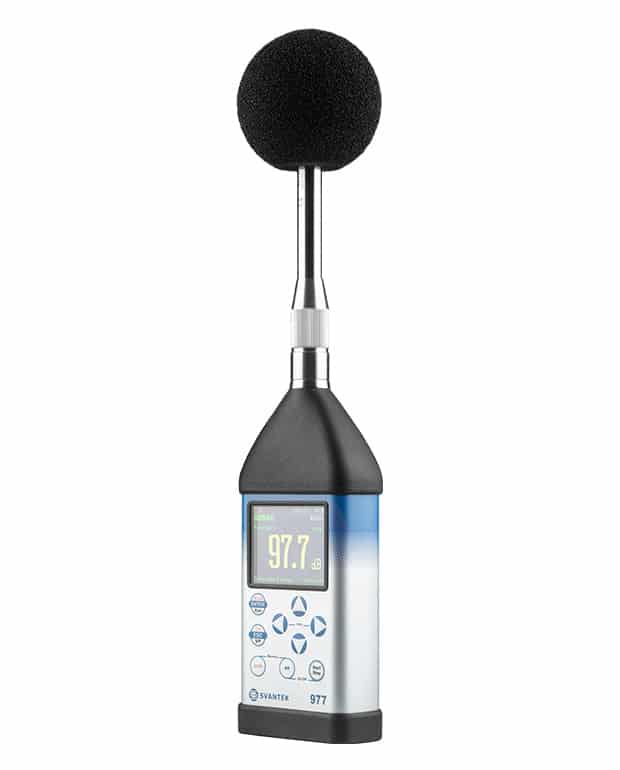
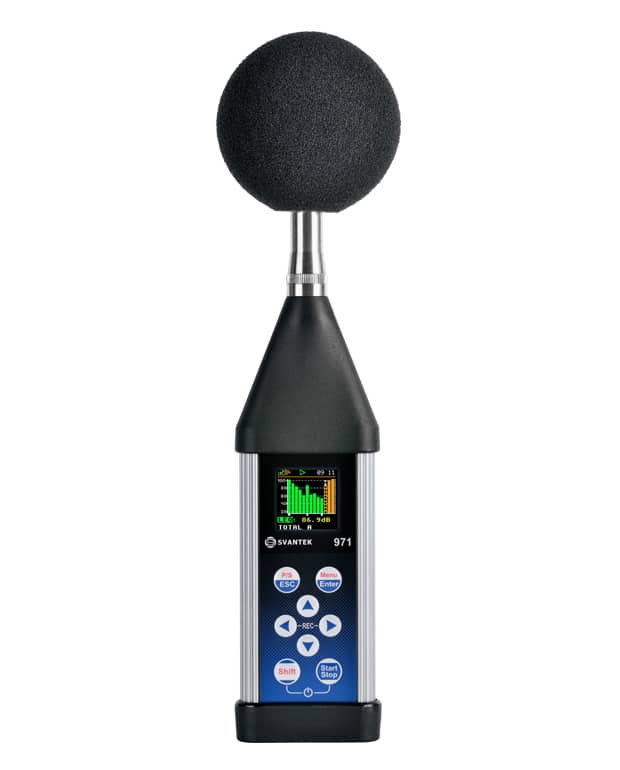
How to choose
the best sound level meter?
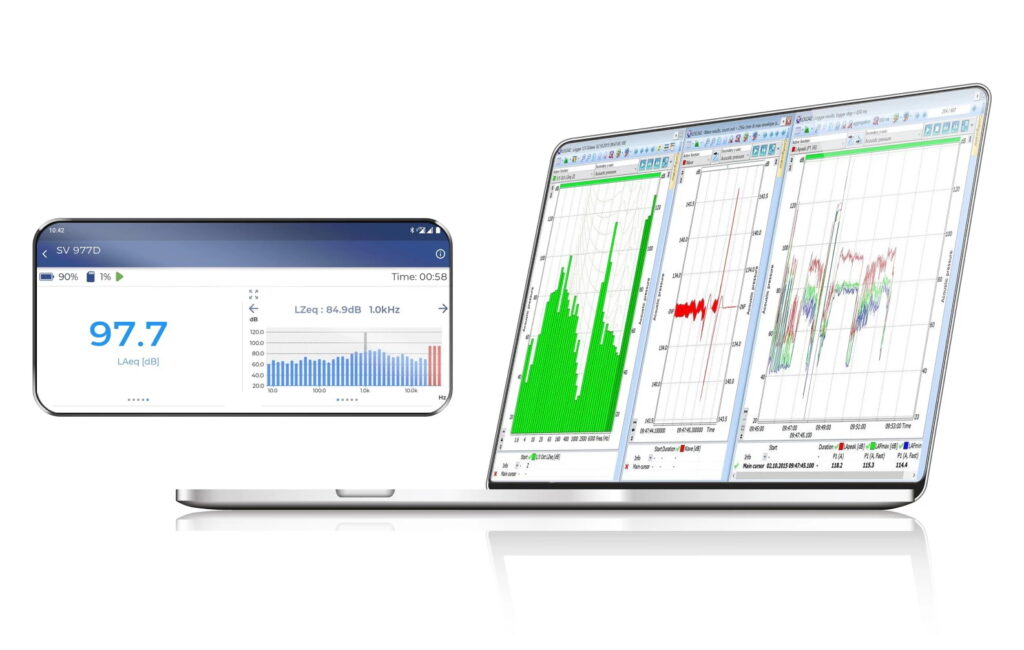
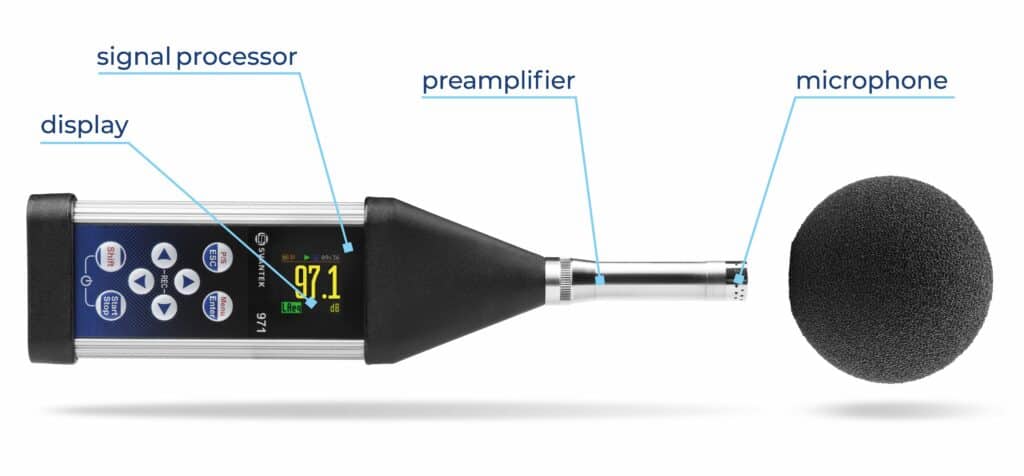
To choose the best sound level meter, consider factors such as accuracy, frequency range, data logging capabilities, and compliance with industry standards like IEC 61672. The ideal meter will depend on your specific needs, whether it’s monitoring workplace noise, conducting environmental assessments, or ensuring public safety in entertainment venues. Always check that the meter complies with relevant regulations to ensure reliable and legally defensible measurements.