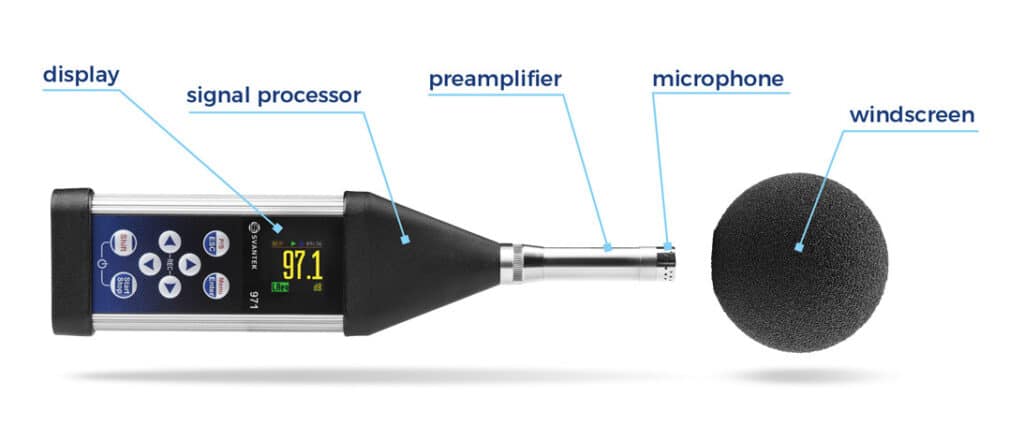
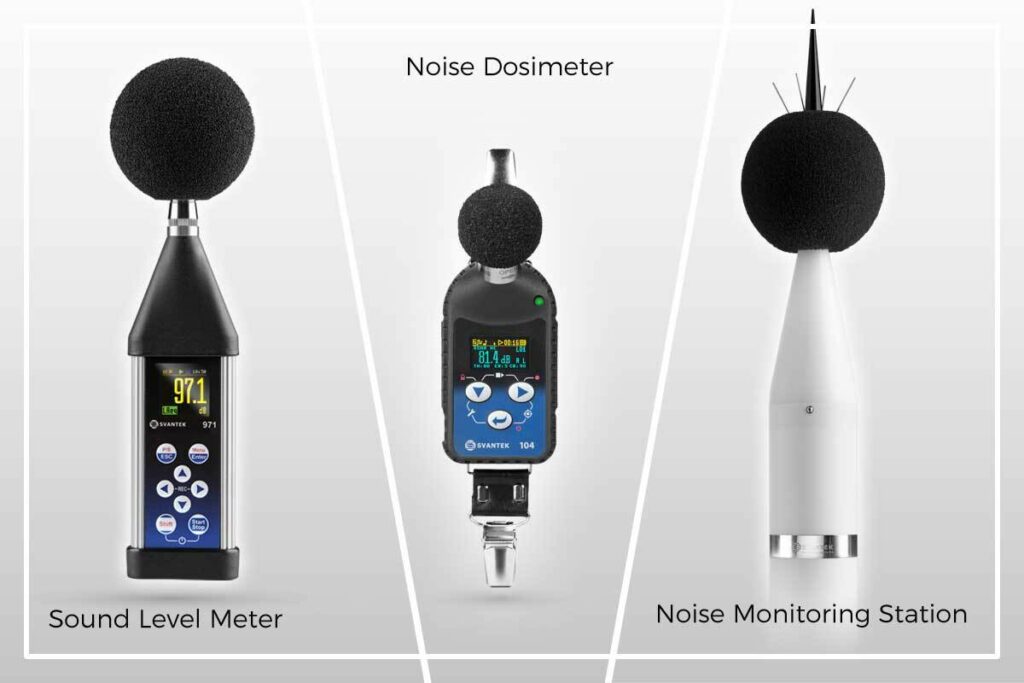
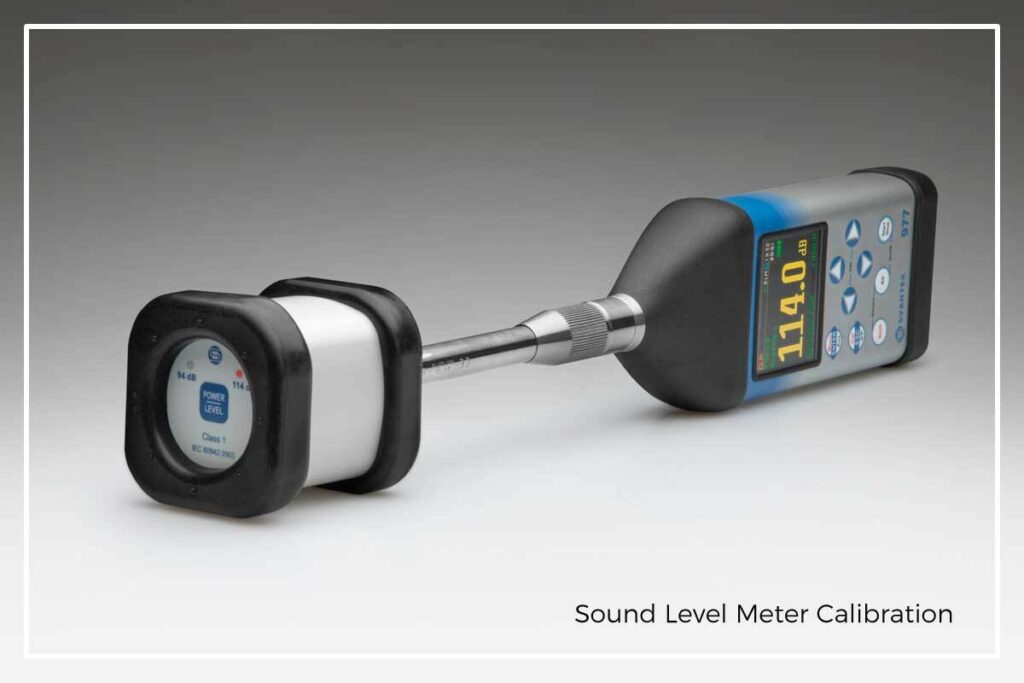
I declare that I have been informed that my data may be transferred to entities that process personal data on behalf of the Administrator, in particular to distributors - such entities process data on the basis of an agreement with the Administrator and exclusively in accordance with its instructions. In such cases, the Administrator requires third parties to maintain the confidentiality and security of information and verifies that they provide appropriate measures to protect personal data.
Some of the entities processing personal data on behalf of the Administrator are established outside the EEA. In connection with the transfer of your data outside the EEA, the Administrator verifies that these entities provide guarantees of a high level of personal data protection. These guarantees stem in particular from the obligation to apply the standard contractual clauses adopted by the Commission (EU). You have the right to request a copy of the standard contractual clauses by sending a request to the Controller.
I declare that I have been informed on my right to withdraw my consent to the processing of my personal data at any time, to access the provided personal data, to rectify, erase, restrict processing and object to the processing of my data, as well as the right to lodge a complaint with the President of the of the Personal Data Protection Office in the event of an infringement of the provisions of GDPR.