Causes of vibration
Vibration is one of the most common issues that can affect machinery, and it can have several causes. One of the most common is missing balance weights. When balance weights are missing, it throws off the rotating component, causing the machine to vibrate. Another common cause of vibration is worn or damaged bearings. When bearings are damaged, they can cause the rotating component to wobble, which also leads to vibration.
What Is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is the process of gathering data from machines while they run to help with decisions on their health, repairs, and potential upgrades before an unanticipated breakdown. The goal of predictive maintenance is to increase profitability by lowering maintenance costs.
Trend Comparison
Comparing the most recent reading to earlier readings for the same measurement Point, which allows you to observe how the Point’s vibration values are “trending” over time, is the most effective and dependable way to assess vibration severity. When the values are presented in a “trend plot,” it is simpler to understand this trend comparison between the current and previous data. A trend plot shows values from the present and the past shown through time. A baseline (known good) reading should be included in measurement records as well. After an overhaul or when other indicators indicate that the machine is functioning properly, the baseline value may be obtained. To identify machinery changes, subsequent data are compared to the baseline.
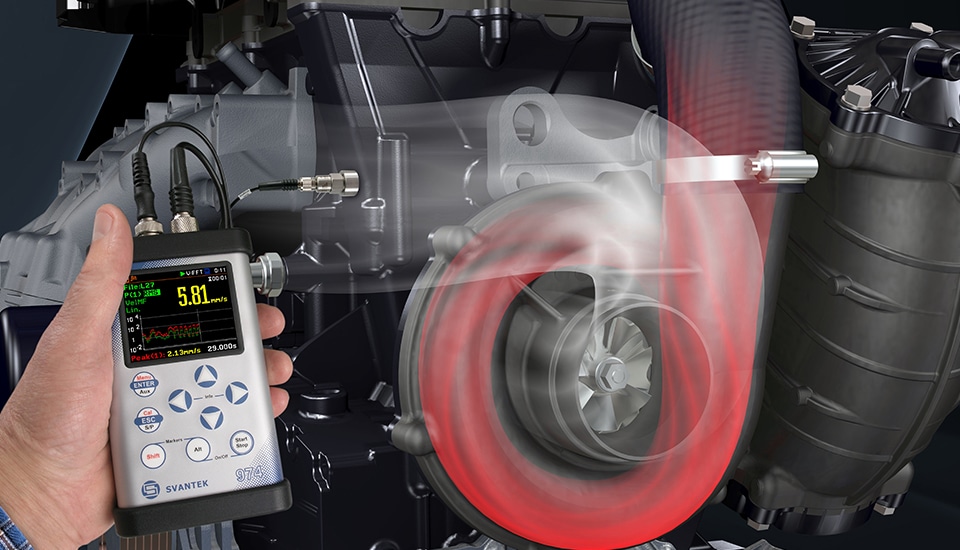
Measurement techniques
Machine vibration measurements are employed for a variety of tasks, including routine operational monitoring, acceptance tests, sophisticated experimental testing, diagnostic and analytical studies, and more. The many different measuring goals result in a wide range of interpretation and evaluation techniques.
Measurements taken on non-rotating parts are sufficient for some machines to characterize their running characteristics in terms of trouble-free operation. Other machine types, like steam turbines, gas turbines, and turbo compressors, can exhibit a variety of vibration modes in the service speed range. Machines in these classes require a more accurate and sensitive way to track changes in vibration conditions, such as shaft vibration measurements.
It is common practice to measure vibration on non-rotating parts or to measure relative shaft vibration, or both. The measurement type for the protection system is normally based on the experience of the machine manufacturer. The measurement of vibration shall be broadband so that the frequency spectrum of the machine is adequately covered.
Vibration measurements on non-rotating parts are generally carried out with a seismic transducer that senses the absolute velocity or acceleration of structure parts on which it is mounted (e.g. the bearing housing). Relative shaft vibration measurements are generally carried out with a non-contacting transducer that senses the vibratory displacement between the shaft and a structural member on which it is mounted (e.g. the bearing housing).
Vibration magnitude
Vibration Magnitude is defined within this group of standards as the maximum value of the broadband RMS velocity in the specified frequency range (typically from 10 to 1,000 Hz), as evaluated on the structure at prescribed points. To assess the machine vibrations the following measurement quantities can be used:
a) vibration displacement, measured in micrometers;
b) vibration velocity, measured in millimeters per second;
c) vibration acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
How do reduce vibration in machines?
To reduce vibration in machines, make sure that all balance weights are in place. Second, check the bearings and replace any that are worn or damaged. By taking these simple steps, you can help to reduce vibration in your machinery and keep it running smoothly.