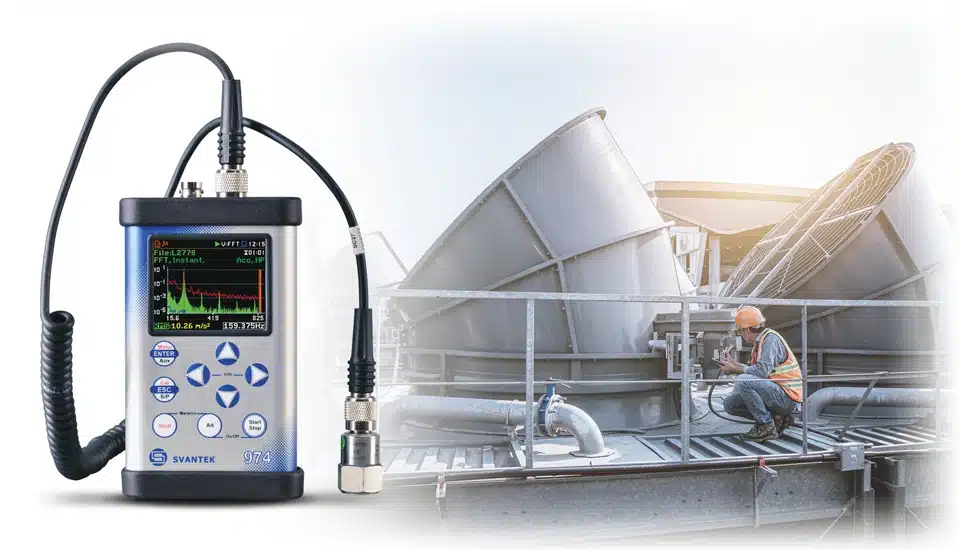
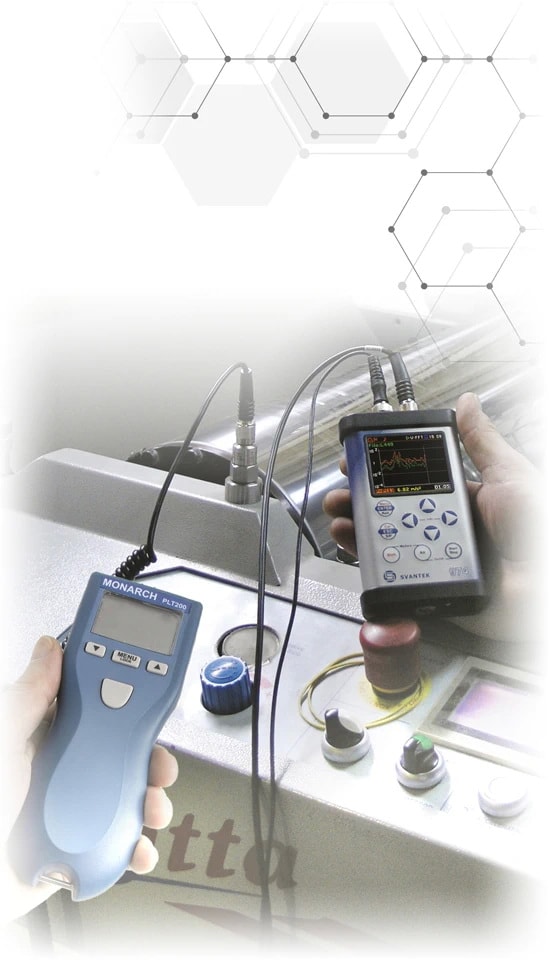
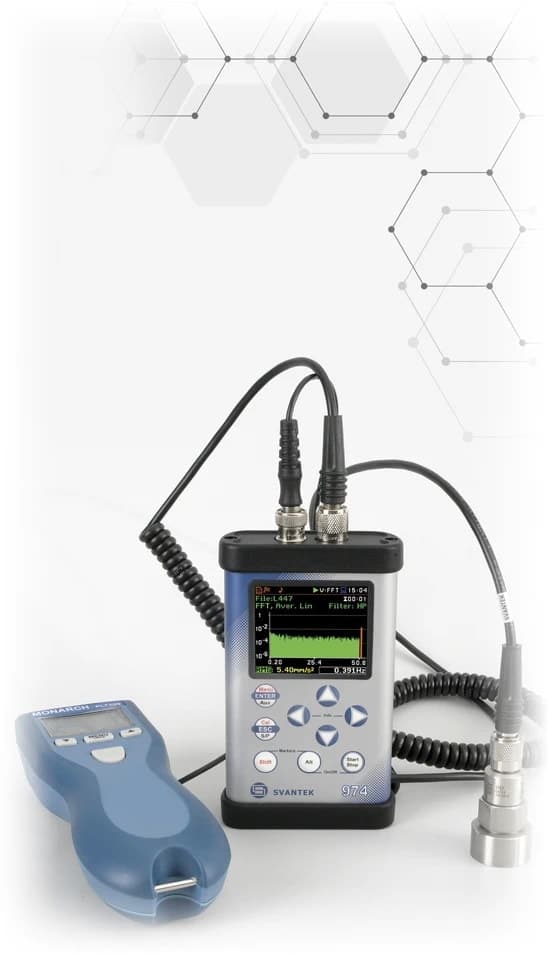
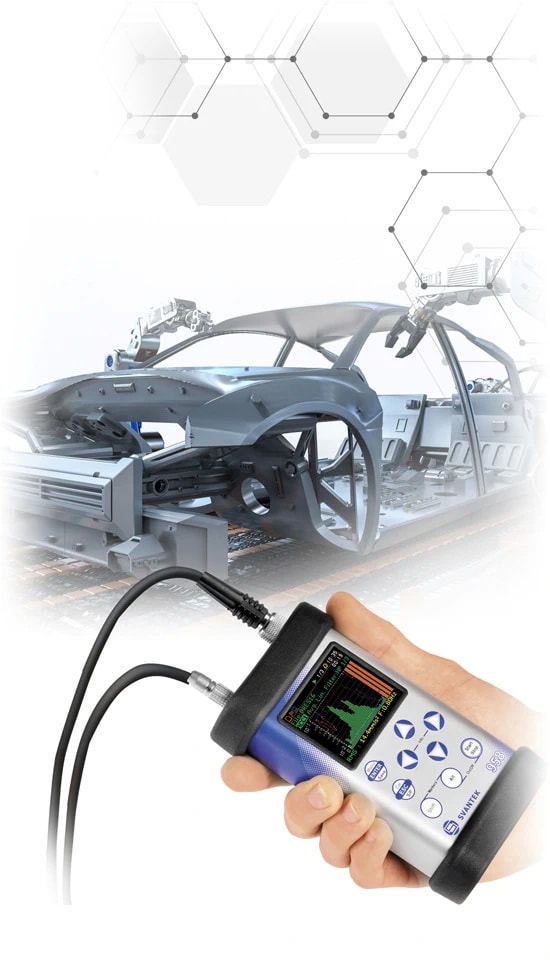
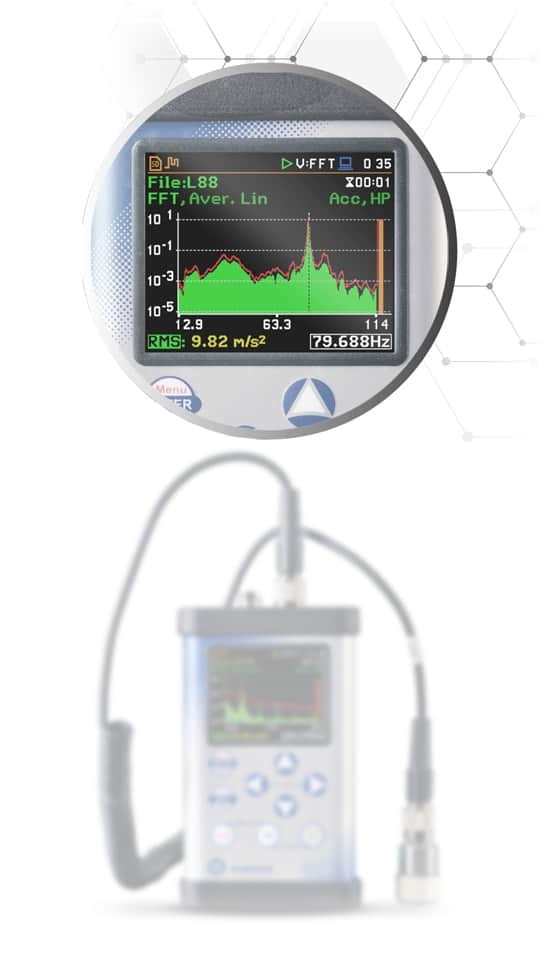
Machine Vibration Measurements
Understanding and managing machine vibration is crucial for the health and performance of industrial machinery. It is a key factor in assessing dynamic conditions, including balancing, bearing flaws, and component stress.